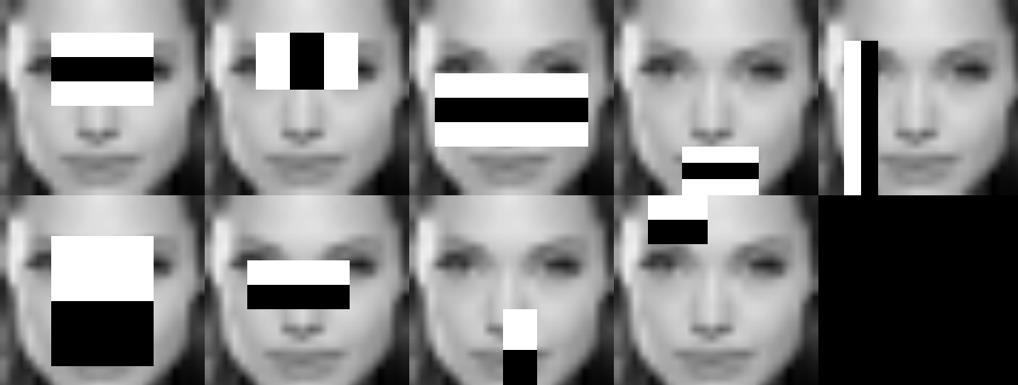DLVR 1 Deep Neural Networks
DLVR 1 Deep Neural Networks
对于作业 常见错误 贴代码截图等
Deep Learning Computer Vision & Robotics Part I. Basic Deep Neural Networks
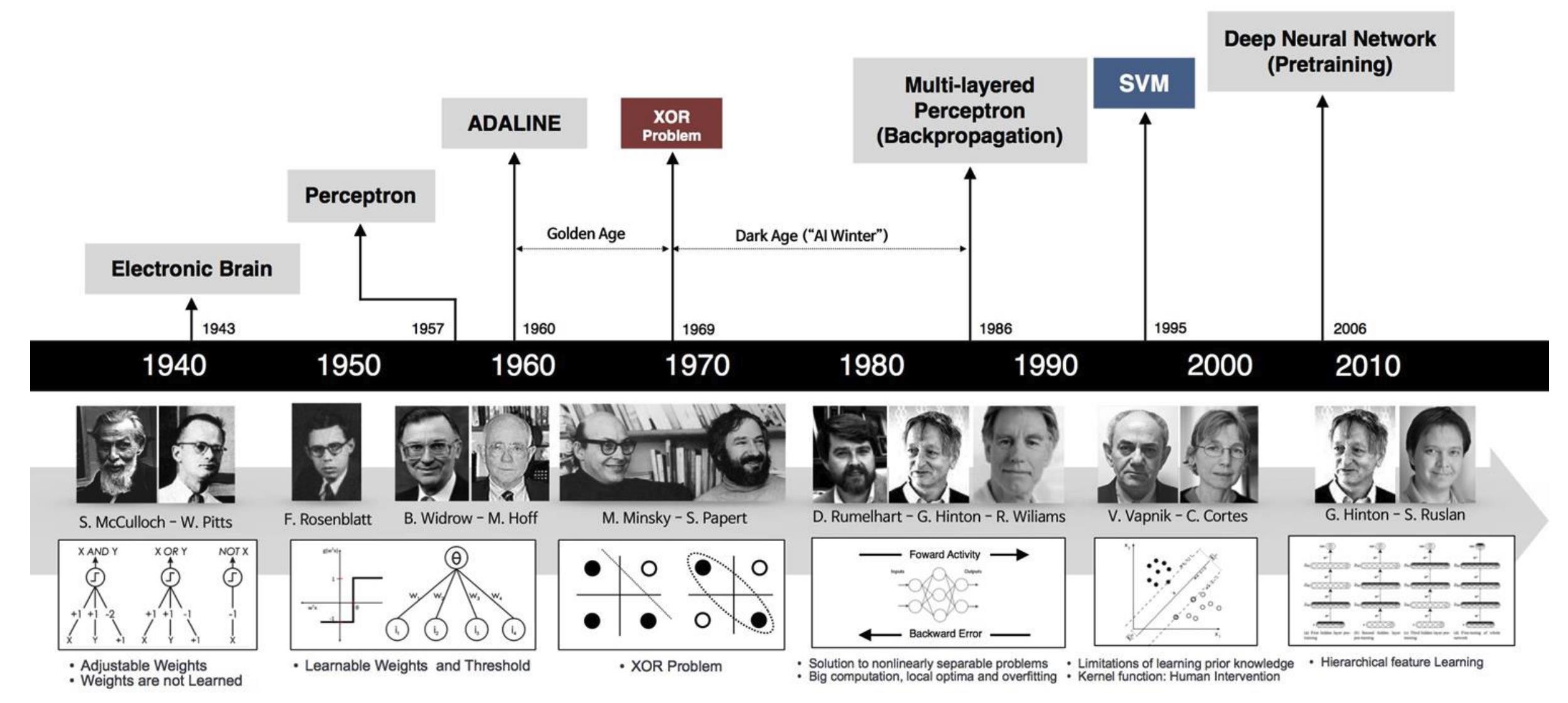
- 1980s - Rediscover Back-propagation
- 1990s - Winter for Neural Networks
- LeNet Handwritten Digits Recognition
- 2000s - Era of Internet & Gaming
- Massive Data & GPGPUs
- 2010s - Early Success & Boom of ANN
- AlexNet (CNN) on ImageNet
- LSTM & Transformers (Attention)
- 2024 - Nobel Prize Winners
- Physics - Artificial Neural Networks
- Chemistry - AlphaFold Protein Design
Background & History-Artificial Intelligence & Neural Networks
“Shallow” Learning Driven AI Era
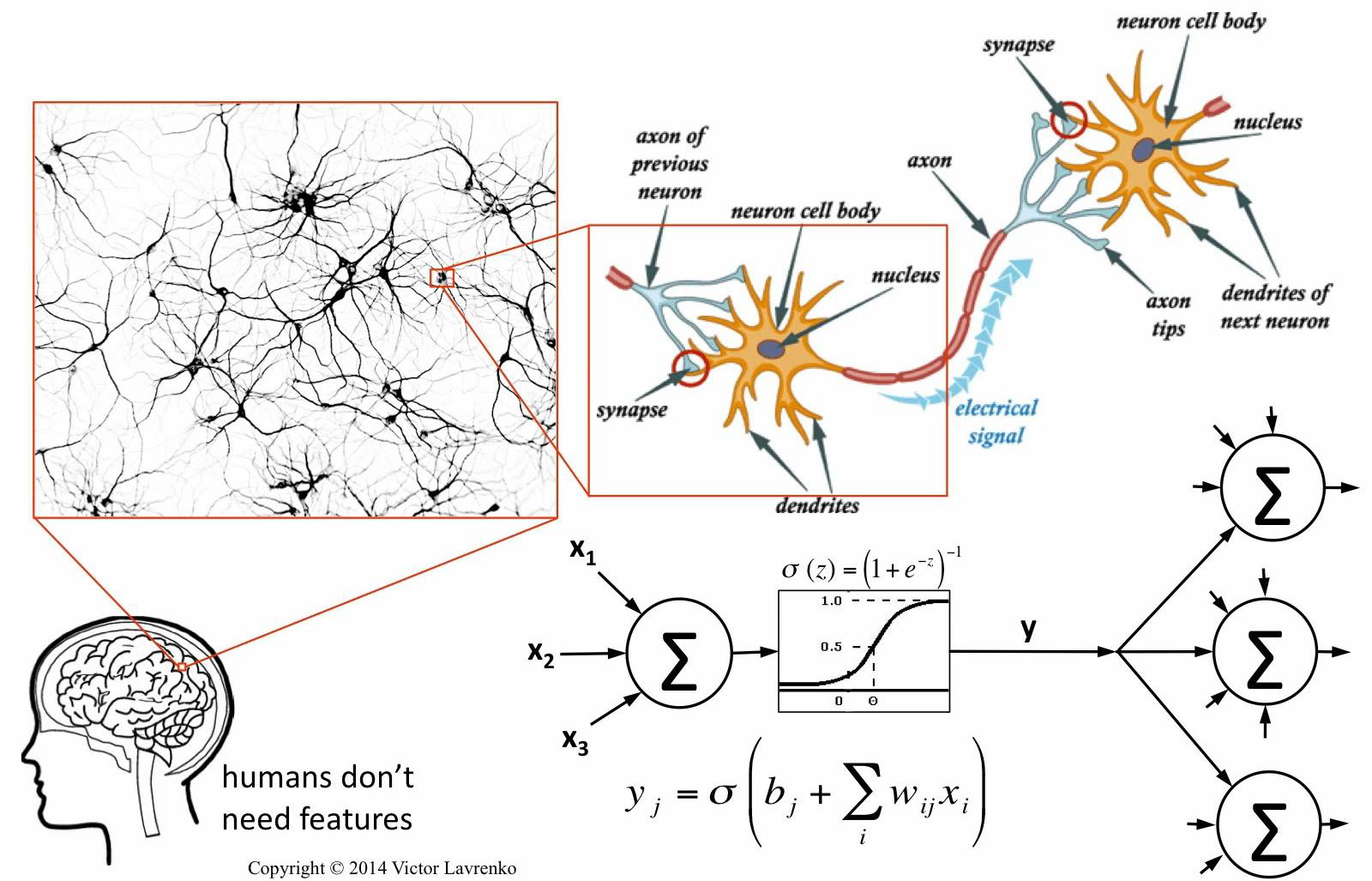
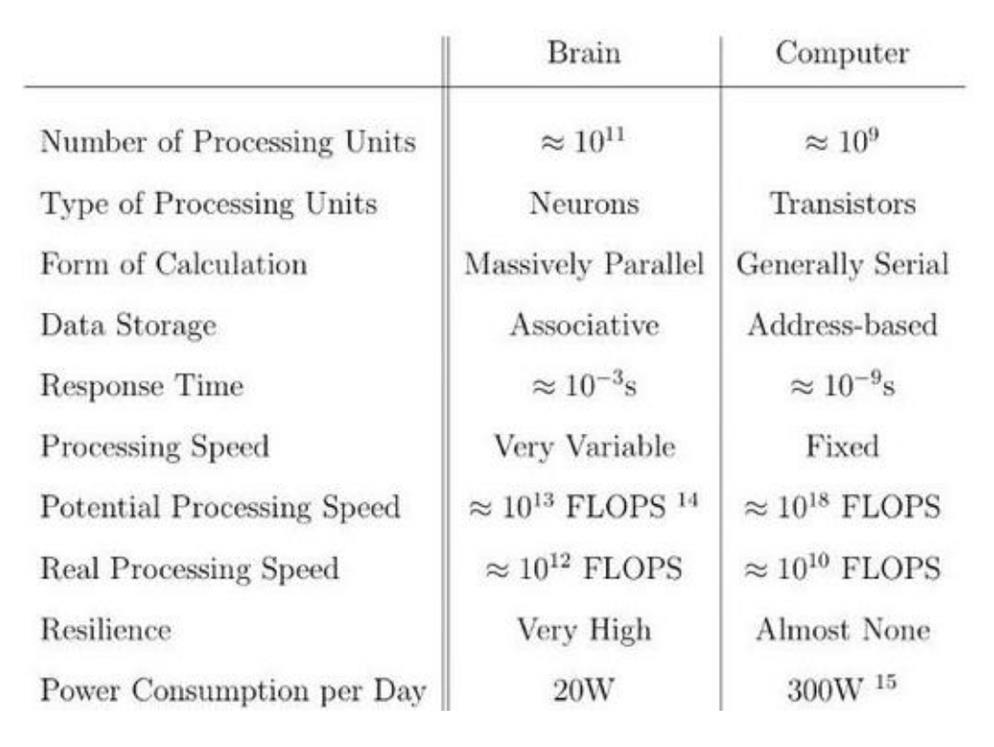
Computational Neuron Model (Neuroscience Inspired)
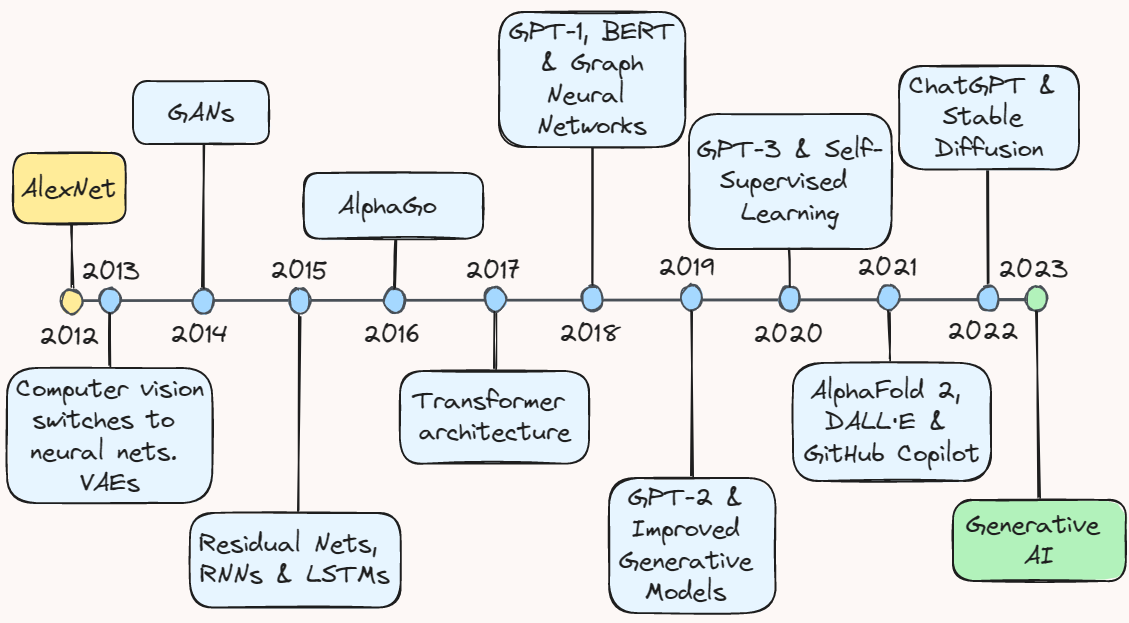
“Deep” Learning Driven AI Era
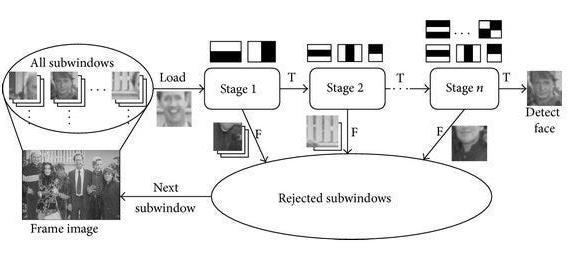
Face Detection: Classic Approach v.s. Deep Learning
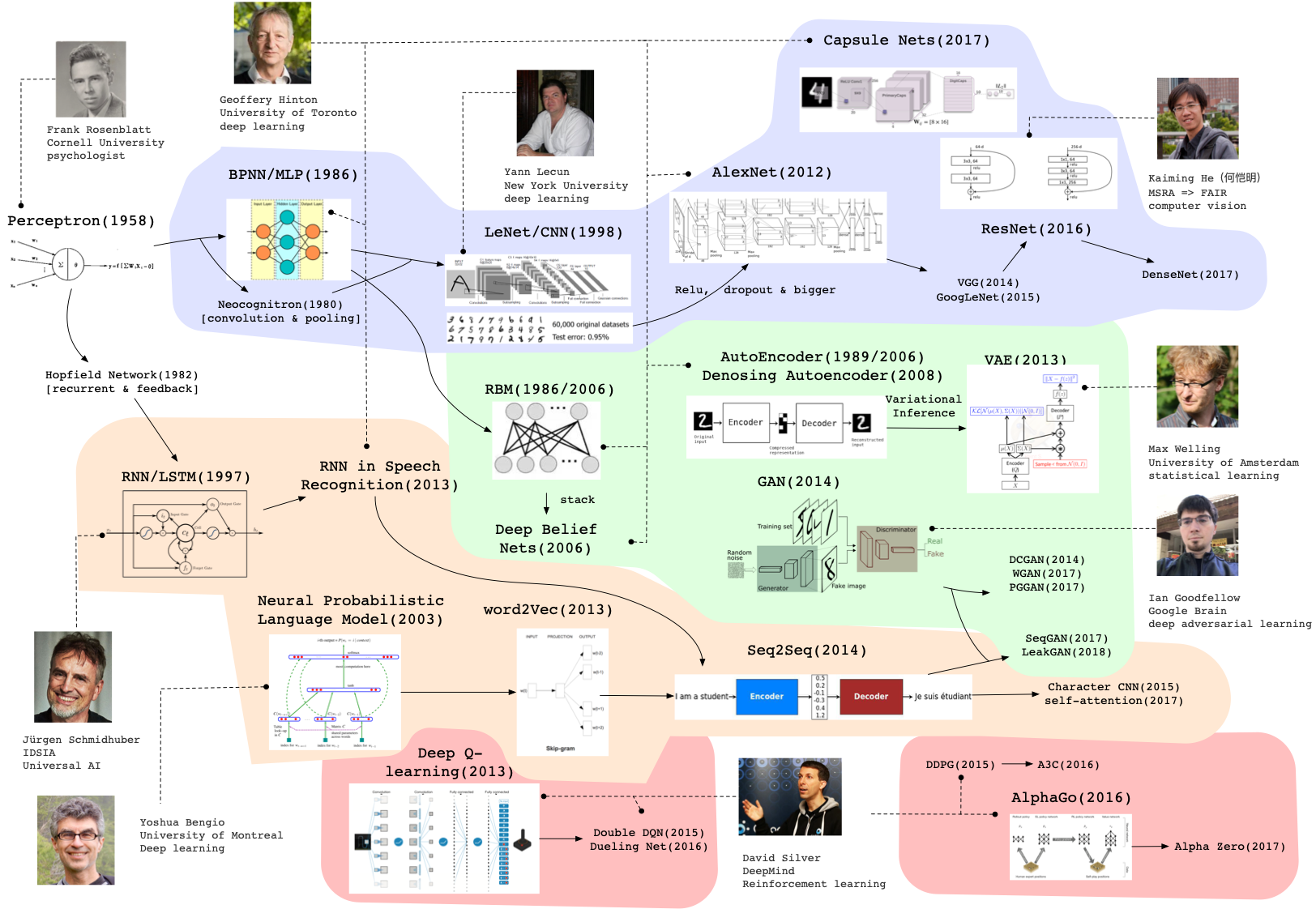
An Incomplete Map of Deep Learning Territory (Until 2023)
Start with “Shallow” NNs
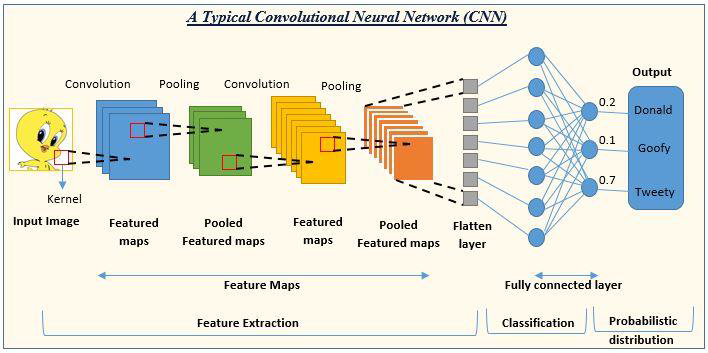
Basic Building Blocks for CNNs
Example 1: Regression Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
This example uses the Boston Housing Dataset to predict the median value of owner-occupied homes (per 1000 dollars). 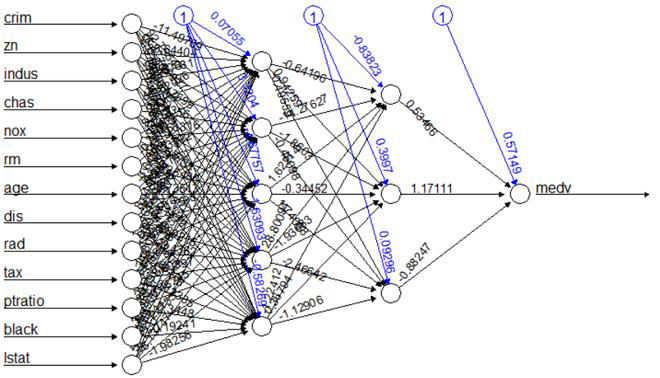
crimper capita crime rate by town.znproportion of residential land zoned for lots over 25,000 sq.ft.indusproportion of non-retail business acres per town.chasCharles River dummy variable (= 1 if tract bounds river; 0 otherwise).noxnitrogen oxides concentration (parts per 10 million).rmaverage number of rooms per dwelling.ageproportion of owner-occupied units built prior to 1940.disweighted mean of distances to five Boston employment centres.radindex of accessibility to radial highways.taxfull-value property-tax rate per $10,000.ptratiopupil-teacher ratio by town.black1000(Bk - 0.63)² where Bk is the proportion of blacks by town.lstatlower status of the population (percent).medvmedian value of owner-occupied homes in $1000s.
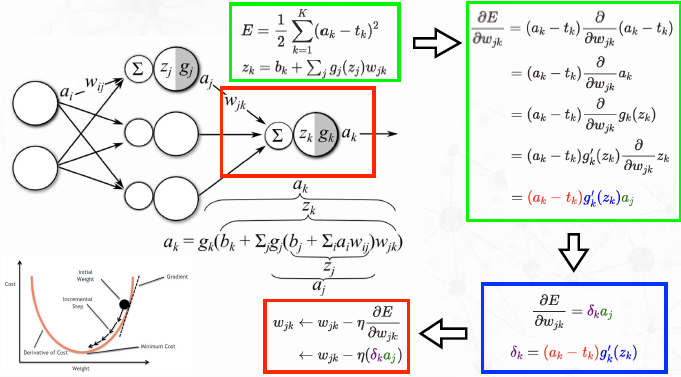
Recap - A Simple Neural Network Model
- $z_j$: input to node $j$ in layer $l$
- $g_j$: activation function for node $j$ in layer $l$ (applied to $z_j$)
- $a_j = g_j(z_j)$: the output/activation of node $j$ in layer $l$
- $b_j$: bias/offset for unit $j$ in layer $l$
- $w_{ij}$: weights connecting node $i$ in layer $(l - 1)$ to node $j$ in layer $l$
- $t_k$: target value for node $k$ in the output layer
 \(E = \frac{1}{2} \sum_{k=1}^{K}(a_k - t_k)^2\) Training Dataset
\(E = \frac{1}{2} \sum_{k=1}^{K}(a_k - t_k)^2\) Training Dataset
| # ID | X1 | Xn | $t_k$ | |——-|——-|——-|————-| | 00001 | ……| ……| …… | | 00002 | ……| ……| …… | | ……| ……| ……| …… | | 99999 | ……| ……| …… |
- https://dustinstansbury.github.io/theclevermachine/derivation-backpropagation
The Output Layer - Gradient Descent
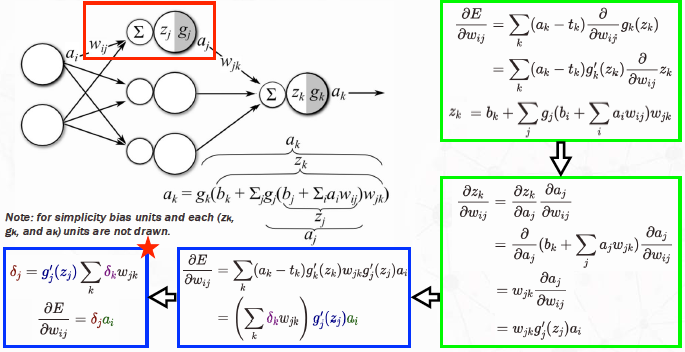
The Hidden Layer - Error Propagation
Back-Propagation
\(\delta_k = (a_k - t_k)g_k'(z_k) \rightarrow \frac{\partial E}{\partial w_{jk}} = \delta_k a_j\)
\[\delta_j = g_j'(z_j) \sum_k \delta_k w_{jk} \rightarrow \frac{\partial E}{\partial w_{ij}} = \delta_j a_i\] This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.