Robotics 3 - Manipulators
From @VergilOP
Lecture 3 - Manipulators
Learning Objectives
Objectives:
- Introduction to Manipulators
- Manipulators and joints
Robotic Manipulators 机械臂
Benefits in repetitive operation:
- Increase volume / capacity 增加容量
- Improve quality and consistency 改进质量
- Untouched by human hand 不能人手触碰
- Reduce wastage 减少浪费
- “Up skilling” of work force 技能提升
A Return On Investment(ROI 回报率) study would be performed to quatify these factors and justify the investment in a bespoke robotics solution
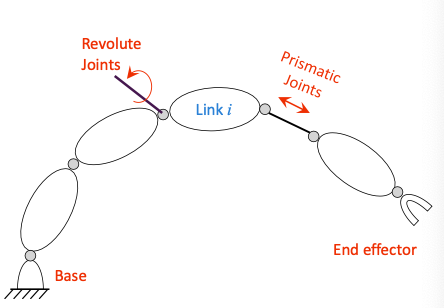
joints 关节
- Different types of joints
- Revolute Joint 旋转关节
- 绕固定轴旋转,自由度(DOF)为1
- Prismatic Joint 伸缩关节
- 可以沿直线滑动,自由度(DOF)为1
- Cylindrical Joint 圆柱关节
- Spherical Joint 球形关节
- Universal Joint 万向关节
- Revolute Joint 旋转关节
Manipulators 机械臂
- Different types of manipulator:
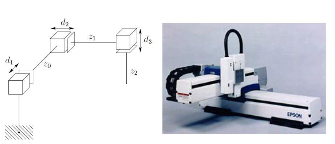
- Cartesian PPP 笛卡尔型
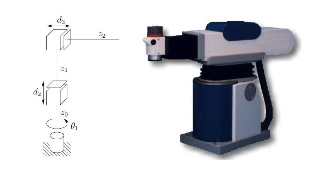
- Cylindrical RPP 圆柱型
- Spherical RRP 球型
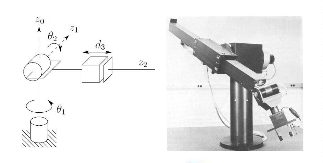
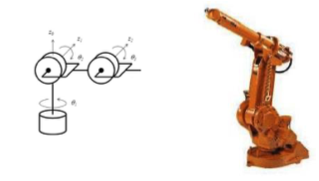
- Articulated RRR 关节型
- SCARA, RRP (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm 选择顺应性装配机械手臂)
Links
- n moving link(s) n个活动连杆
- 1 fixed link 固定基座
- joints
- Revolute (1 DOF)
- Prismatic (1 DOF)
- Position Parameters 位置参数
- Position parameters describe the full configuration of the system
n links -> 9n parameters (3 vectors: Each vector has 3 parameters)
Generalised coordinates: A set of independent configuration parameters **Degreee of Freedom**: Number of generalised coordinates
- We need 6 DOF to have access to all space
- 3 DOF: Position 位置
- 3 DOF: Orientation 姿态
Revolute and prismatic joints have 1 DOF
Generalised coordinates 广义坐标
A set of independent configuration parameters 独立参数
Each rigid body(刚体) needs 6 parameters to be described
- 3 positions
- 3 orientations
For n rigid body, we need 6n parameters
Constrains myst be applied:
- Each joint has 1DOF, so 5 constrains will be introduced
n moving links -> 6n parameters
n joints -> 5n constrains
n DOF
This is for manipulator with fixed base
End effectors configuration 末端执行器配置
End effector is the last rigid-body and it has all the freedom from previous links
A set of parameters describing position and orientation of the end effector: $(x_1, x_2, x_3, … , x_m)$ with respect to {0}
$O_{n+1}$: is operational coordinates(task coordinates)
A set of $x_1, x_2, x_3, … , x_{m_o}$ of $m_o$ independent configuration parameters
$m_o$ is number of DOF of the end effector, max 6 DOF 末端执行器自由度最高为6
End effector, Joint coordination 末端执行器,关节坐标
- Joint space (configuration space) is the space that a manipulator is represented as a point.
- (x,y) is a vector for position of end effector $\alpha$ defines orientation(angle) of end effector
- Defines: operational coordinates -> operational space
Redundancy 冗余
- A manipulator is Redundant if \(n>m\) n number of DOF of the manipulator
m number of DOF of the end effector(operational space)
Degreee of Redundancy: n - m
- A manipulator is Redundant if \(n>m\) n number of DOF of the manipulator
冗余(Redundancy):
- 定义:
- 当机械臂的自由度数$n$大于末端执行器所需控制的自由度数$m$*时,称该机械臂是*冗余的。
- 数学表达式: n>mn > mn>m
- 参数说明:
- $n$:机械臂的自由度数量,即关节的数量。
- $m$:末端执行器在操作空间中的自由度数量,最大为6。
- 冗余度:
- 冗余度 = $n - m$。
- 表示机械臂拥有的额外自由度数量。
冗余机械臂的优势:
- 避障能力:
- 由于有额外的自由度,机械臂可以在完成主要任务的同时避开工作空间中的障碍物。
- 灵活性:
- 可以实现更优化的运动,例如最小化能量消耗、避免奇异点或优化机械臂的姿态。
- 多任务处理:
- 能够同时满足多个次要任务的要求,例如保持特定的姿态或力。