Robotics 4 - Kinematics
From @VergilOP
Lecture 4 - Kinematics
Learning Objectives
Objectives:
- Spatial Description
- Transformation
- Rotation
- Translation
Spatial Description 空间描述
- Position of a Point 点的位置
- With respect to a fixed origin O, the position of a point P is described by the vector OP(p)
相对于固定原点 O,点 P 的位置由向量 OP(p) 描述
- With respect to a fixed origin O, the position of a point P is described by the vector OP(p)
- Coordinate Frames:
- Rotation
- Translation
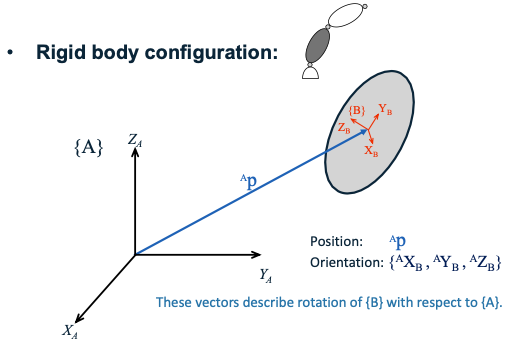
- Rigid body configuration:
- Position: $^AP$
- Orientation: ${^AX_B, ^AY_B, ^AZ_B}$
These vectors describe rotation of {B} with respect to {A}
Transformation
Rotation
Rotation Matrix:
旋转矩阵(Rotation Matrix)用于描述坐标系之间的旋转关系。假设有两个坐标系${A}$和${B}$,旋转矩阵$^A_BR$表示从坐标系${B}$到坐标系${A}$的旋转。 \(^A_BR = \begin{bmatrix} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} ^A \hat{X}_B & ^A \hat{Y}_B & ^A \hat{Z}_B \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} {^B \hat{X}_A}^T \\ {^B \hat{Y}_A}^T \\ {^B \hat{Z}_A}^T \end{bmatrix} = {^B_A R}^T = \begin{bmatrix} \hat{X}_B \cdot \hat{X}_A & \hat{Y}_B \cdot \hat{X}_A & \hat{Z}_B \cdot \hat{X}_A\\ \hat{X}_B \cdot \hat{Y}_A & \hat{Y}_B \cdot \hat{Y}_A & \hat{Z}_B \cdot \hat{Y}_A\\ \hat{X}_B \cdot \hat{Z}_A & \hat{Y}_B \cdot \hat{Z}_A & \hat{Z}_B \cdot \hat{Z}_A \end{bmatrix}\)
表达式 基向量组合形式 转置形式 点积形式
$^B \hat{X}_A$表示在坐标系${B}$中,坐标系${A}$的X轴单位向量。同理,其他项以此类推。
$\hat{X}_B$、$\hat{Y}_B$、$\hat{Z}_B$是坐标系${B}$的单位基向量,$\hat{X}_A$、$\hat{Y}_A$、$\hat{Z}_A$是坐标系${A}$的单位基向量。
旋转矩阵是一个正交矩阵(Orthogonal Matrix),其转置等于其逆矩阵。
- Inverse of Rotation Matrix(Orthonormal Matrix) \(^A_BR^{-1} =\ ^B_AR =\ ^A_BR^T\)
State description: $^A\hat{X}_B = ^A_BR\ \ ^B\hat{X}_B$
Dot product: 通过点积,可以计算基向量在不同坐标系中的投影关系。 \(^A \hat{X}_B = \begin{bmatrix} \hat{X}_B \cdot \hat{X}_A \\ \hat{X}_B \cdot \hat{Y}_A \\ \hat{X}_B \cdot \hat{Z}_A \end{bmatrix}\\ ^A \hat{Y}_B = \begin{bmatrix} \hat{Y}_B \cdot \hat{X}_A \\ \hat{Y}_B \cdot \hat{Y}_A \\ \hat{Y}_B \cdot \hat{Z}_A \end{bmatrix}\\ ^A \hat{Z}_B = \begin{bmatrix} \hat{Z}_B \cdot \hat{X}_A \\ \hat{Z}_B \cdot \hat{Y}_A \\ \hat{Z}_B \cdot \hat{Z}_A \end{bmatrix}\) 其中,每个元素表示${B}$的基向量在${A}$的基向量方向上的投影。例如,$\hat{X}_B \cdot \hat{X}_A$表示${B}$的X轴在${A}$的X轴方向上的投影。
Description of a Frame:
- 描述一个坐标系需要知道其基向量和原点位置:
- 坐标系${B}$在${A}$中的表示包括:
- 基向量:$^A \hat{X}_B$、$^A \hat{Y}_B$、$^A \hat{Z}_B$
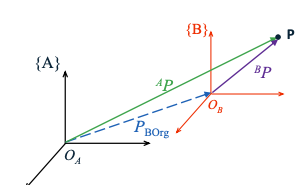
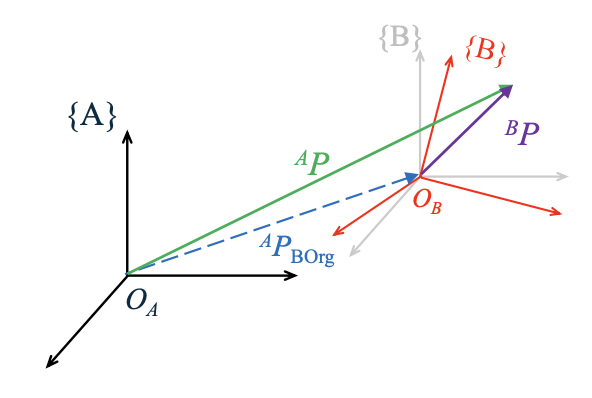
- 原点位置:$^A P_{B_{\text{org}}}$
- 坐标系${B}$在${A}$中的表示包括:
- Frame{B}: $^A \hat{X}B$, $^A \hat{Y}_B, ^A \hat{Z}_B$, $^AP{Borg}$
- 这里,$^A_BR$是从${B}$到${A}$的旋转矩阵,$^A P_{B_{\text{org}}}$是${B}$的原点在${A}$坐标系中的位置向量。
- 描述一个坐标系需要知道其基向量和原点位置:
Mapping:
- Changing descriptions from frame to frame
- 映射是指将一个向量从一个坐标系转换到另一个坐标系。
- 旋转变换:
- 当我们知道向量在${B}$坐标系中的表示$^B P$,想要得到它在${A}$坐标系中的表示$^A P$,可以使用旋转矩阵进行变换。
- 假设有一个向量$P$,它在坐标系${B}$中的表示为$^B P$。我们想要计算它在坐标系${A}$中的表示$^A P$。
- 首先,利用${B}$和${A}$的基向量之间的关系:
- If $P$ is in ${B}$: $^BP$
\(^AP =\ ^A_BR\ ^BP\)
- 这意味着,可以直接使用旋转矩阵$^A_BR$将向量从${B}$坐标系转换到${A}$坐标系。
- 假设有一个向量$P$,它在坐标系${B}$中的表示为$^B P$。我们想要计算它在坐标系${A}$中的表示$^A P$。
Translation 平移
\[^AP_{OA} = ^AP_{OB} + ^AP_{BOrg}\]General Transformation
$^A P$:点$P$在坐标系${A}$中的表示。
$^B P$:点$P$在坐标系${B}$中的表示。
$^A_B R$:从${B}$到${A}$的旋转矩阵。
$^A P_{B_{\text{org}}}$:坐标系${B}$的原点在${A}$中的位置。
Homogeneous Transformation: 齐次变换矩阵
统一旋转和平移 \(^AP_{(4\times1)} =\ ^A_BT_{(4\times4)}\ ^BP_{(4\times1)}\)
$^A_B T$是齐次变换矩阵,包括旋转和平移。
General Operators: \(P_2 = \begin{bmatrix} R_k(\theta) & Q \\ 0\ 0\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}P_1\)
\[P_2 = T\ P_1\]
$P_1$:初始点的齐次坐标表示。
$P_2$:变换后的点的齐次坐标表示。
$R_k(\theta)$:绕轴$k$旋转$\theta$角度的旋转矩阵。
$Q$:平移向量。
Inverse Transform 逆变换 \(^A_B T = \begin{bmatrix} ^A_B R & ^A P_{Borg} \\ 0\ 0\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\)
\[^A_B T^{-1} = ^B_A T = \begin{bmatrix} ^A_B R^T & -^A_B R^T \cdot\ ^AP_{Borg} \\ 0\ 0\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\]Homogeneous Transform Interpretations:
Description of a frame 坐标系的描述
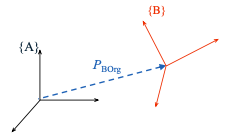 \(^A_BT:\{B\} = \{^A_BR\ \ ^AP_{Borg}\}\)
\(^A_BT:\{B\} = \{^A_BR\ \ ^AP_{Borg}\}\)Transform operator 变换算子
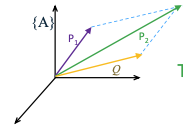 \(T: P_1 \rightarrow P_2\) $P_1$:初始点。
\(T: P_1 \rightarrow P_2\) $P_1$:初始点。$P_2$:经过变换后的点。
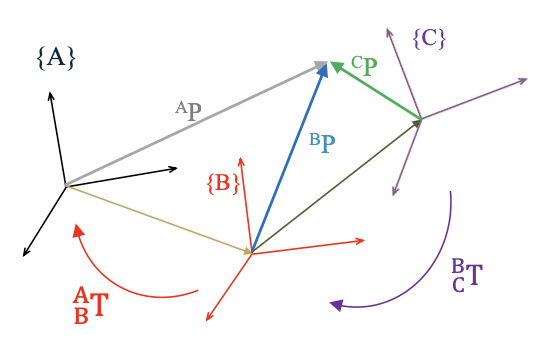
Compound Transformation:复合变换
\[^BP = ^B_C T \ C_P\] \[^AP = ^A_B T \ B_P\] \[^AP = ^A_B T \ ^B_C T \ C_P\] \[^A_C T = ^A_B T \ ^B_C T\] \[^A_C T = \begin{bmatrix} ^A_B R \ ^B_C R & ^A_B R \ ^B P_{Corg} + ^A P_{Borg} \\ 0\ 0\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\]Transform Equation
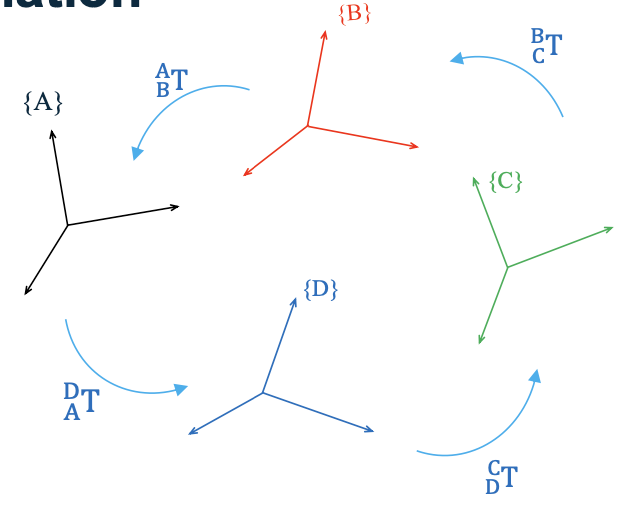
- 在多个坐标系之间的循环变换中,变换矩阵的乘积应等于单位矩阵:
Representations
End-effector Configuration 末端执行器的齐次变换矩阵:
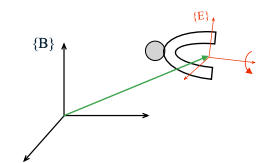 \(^B_ET: Position + Orientation\) $^B_E T$表示末端执行器相对于基座坐标系${B}$的齐次变换矩阵,包含了位置和姿态的信息
\(^B_ET: Position + Orientation\) $^B_E T$表示末端执行器相对于基座坐标系${B}$的齐次变换矩阵,包含了位置和姿态的信息End-effector configuration parameters: \(X = \begin{bmatrix} X_P \\ X_R \end{bmatrix}\) $X_P$:位置参数,表示末端执行器在空间中的位置。
$X_R$:姿态参数,表示末端执行器在空间中的方向或旋转。
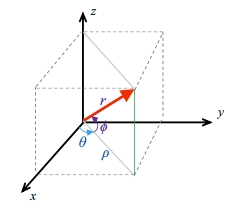
- Cartesian: (x, y, z) 笛卡尔坐标系
- Cylindrical: $(\rho, \theta, z)$ 圆柱坐标系
- Spherical: $(r, \theta, \phi)$ 球坐标系